
The impact of regulatory changes on banking technology and how banks are adapting
Regulatory compliance protects the institution’s integrity and industry standing by ensuring that the bank operates according to regulations. Protecting bank data, preventing government fines and tax evasion, monitoring and reporting anti-money laundering activities, assessing risks, and ensuring zero violations of banking ethics are all responsibilities of this function.
The regulatory function accomplishes its rigorous objectives through proactive communication of the compliance policy to personnel, enforcement of an ethical bank culture, and standardization of processes.
As a result of the 2008 financial crisis, banks are confronted with a reporting burden that continues to grow. Although supervisors recognize and strive to mitigate these burdens, forthcoming reporting requirements are concerning due to a shift in supervisory attention towards addressing climate change risks and the corresponding sustainability reporting.
To improve their ‘data-driven supervision’ capabilities and safeguard consumers, local regulators plan to augment their data queries to participants in the financial markets. Traditional banks are under increasing pressure to reassess their business models and transition into future-proof, data-driven organisations due to the concurrent pursuit of competitive advantage and technological advancements.
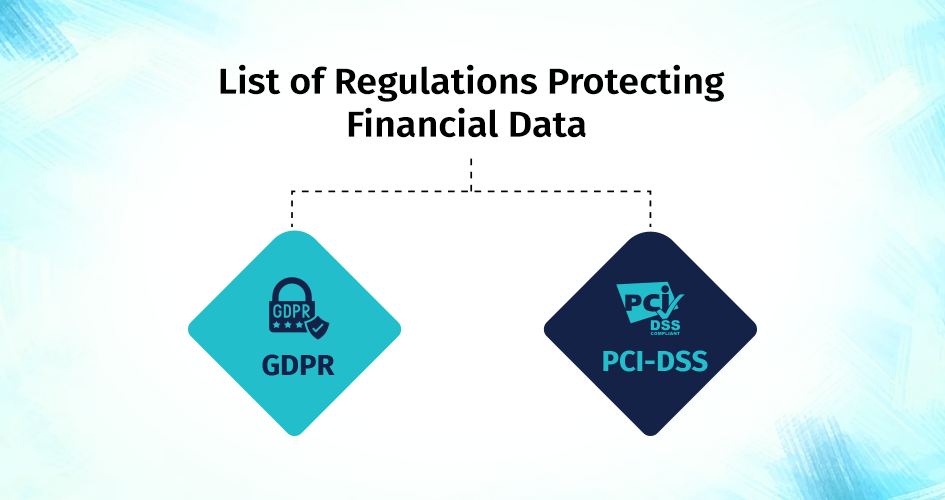
List of Regulations Protecting Financial Data
GDPR (GDPR): The GDPR of the European Union is stringent. EU data and online anonymity are managed by it.
PCI-DSS (PCI DSS): Consumer data is safeguarded by financial data security standards. The process, storage, and transmission of cardholder data are standardized.
Financial institutions are required to disclose their data-sharing policies by Gramm-Leach-Bliley (GLBA) to protect vital data.

Legislation Governing Financial Compliance
The Act governs the recording and disclosure of financial information by organizations. It will combat corruption and corporate fraud. Prioritizing cybersecurity measures is crucial to complying with regulations and safeguarding financial data from potential harm.
AML Directives: AML directives serve to prevent the financing of terrorism and money laundering. It aids in the uniformity of regulations. It governs the financial markets and protects investors. It standardizes practices in financial services.
The Expansion of Regulatory Compliance’s Application in Banking
With the evolution of technology and consumer preferences, there is an increasing need for businesses to adhere to regulatory compliance. There were no internet or digital assets decades ago. Such factors stimulate the economy. Effective laws are therefore required for the welfare of both consumers and businesses. Unsurprisingly, regulatory compliance is currently a top priority for businesses. Data losses and security vulnerabilities are diminished by compliance. License revocation, monetary penalties, reputational harm, and excessive customer attrition are all avoidable through compliance.
Before discussing potential strategies for banks to overcome these obstacles, it is prudent to examine three critical factors that unequivocally demonstrate the necessity for banks to adopt a genuinely data-driven business model.
Numerous new reporting requirements have been imposed on banks since the financial crisis to furnish regulatory authorities with the data necessary for the execution of their supervisory responsibilities. This report contains increasingly comprehensive statistical information and prudential and resolution data. In accordance with the principle of proportionality, which is enforced by supervisory authorities, sizable institutions are obligated to disclose more than ten times the quantity of data points as their more modest counterparts. However, according to these smaller institutions, EBA supervisory reporting represents nearly forty per cent of their overall compliance expenses.
Principal contributors to these expenditures are:
The consistency and stability of the EBA’s supervisory structure and definitions.
A considerable proportion of financial institutions consider the swift evolution of reporting obligations and impromptu, non-standardized reporting requests to affect compliance expenses substantially. Regulators increasingly emphasise financial institutions’ internal IT infrastructure and governance to enhance data integrity and control.
Supervisors are influenced by regulatory pressures and the expenses associated with compliance to promote greater standardization and harmonization in reporting obligations and data submissions. It presents an exceptional opportunity for institutions to revaluate their current IT and data infrastructure and overall reporting and data strategy.
Smaller organizations frequently hesitate to implement FinTech in their reporting procedures, whereas larger organizations need help integrating new technologies into their extensive and intricate legacy data architectures. Due to their lack of critical mass, these are considered prohibitively expensive and unsuitable for extensive implementation.
In addition, recent developments in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics are compelling institutions to reconsider their data architectures. Unique opportunities exist with serverless platforms, modular design, and containerization to increase speed and adaptability, both of which are critical in an environment that is perpetually evolving.
Many prominent banks are adopting a comprehensive strategy for deploying advanced data analytics to gain a competitive advantage. FinTechs are particularly dominant in the implementation of novel technologies. They construct scalable data infrastructures and conduct business with a “digital first” mentality. It gives them a competitive advantage regarding the execution of data-driven procedures and the creation of new products. Furthermore, it empowers them to employ AI-driven decision-making in customer engagement, reporting, and risk management.
In addition to the emergence of FinTech as a formidable competitor, the reduction of intermediaries using digital ecosystems and large technology companies is facilitating the disintermediation of conventional financial services. These services provide existing banking clients with an integrated and highly personalized experience by facilitating access through a single-entry point. Large technology companies possess significant competitive advantages due to their access to vast quantities of consumer data and their inherent capacity to scale innovative technologies. These tech titans have recently been observed attempting to expand into adjacent industries, including payments, insurance, and the mortgage market.
Banks should embrace an integrated way of thinking to confront the challenges of this complexity. It begins with the fundamental treatment of data as an asset instead of a liability.

Initial Precautions Regarding Regulatory Compliance
Conduct a comprehensive compliance audit to identify the deficiencies and inefficiencies within the organization.
Evaluating the qualitative and quantitative effects on your organization. Practical measures for enhancement are derived from this exercise.
Designating a Chief Compliance Officer: The responsibility of a Corporate Compliance Officer is to uphold the ethical standards, commitment, and integrity of the organization.
Establishing Internal Company Policies: By formalizing compliance manuals and conducting regular self-evaluation exercises, personnel can remain well-informed regarding many regulations.
Regulatory Compliance Training: It is essential to educate employees on any modifications or revisions to an organization’s compliance policies.
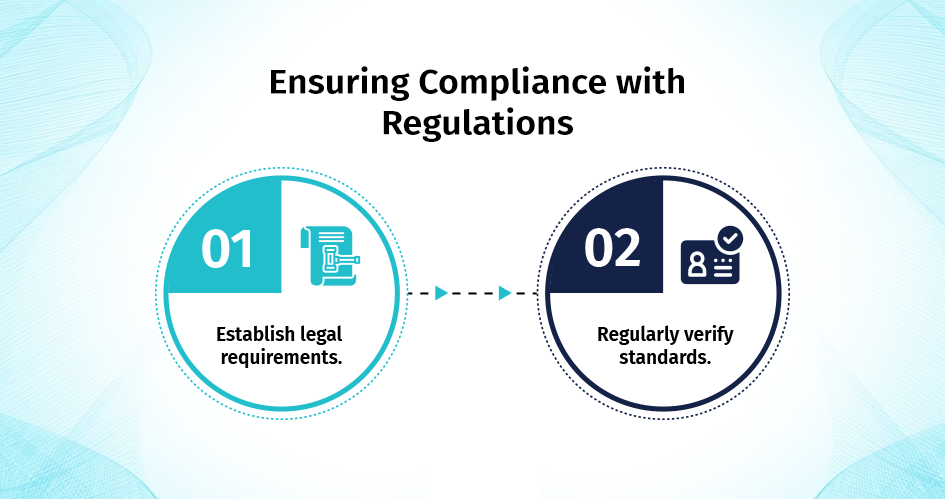
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
The process of ascertaining which laws impact a company according to its region and industry.
Establish legal requirements: The business and its operations determine each law’s compliance obligations. Evaluate obligations related to adherence.
Adequate documentation demonstrates how business practices adhere to regulatory compliance standards, mitigating the risk of incurring penalties during audits.
Regularly verify standards: Cybersecurity regulations diverge. Maintain compliance by monitoring compliance requirements.
Conclusion
Marketing in financial services is subject to stringent regulations, with good reason. Most financial services organizations have had their meticulously devised strategies thwarted by legal or compliance matters. Understanding complete regulatory restrictions enables FIs to develop strategies and operations around them instead of allowing them to impede innovation.
Banks must contend with an ever-evolving environment. Technological advancements, including AI and analytics, are transforming their business models. Some financial institutions cannot fully take advantage of these developments, unlike digitally native banks.
How Can Datavision help?
We assist various financial institutions and global banks on their digital transformation journey. Our one-of-a-kind approach, which combines people, process, and technology, expedites the delivery of superior results to our clients and drives excellence. Several reputed companies leverage our proprietary suite of business excellence tools and services to unlock new growth levers and unparalleled ROI.
Datavision stands proudly as a prominent banking software solutions provider, recognized for our unwavering commitment to excellence in the industry. We have earned our esteemed reputation by consistently delivering cutting-edge core banking software, catering to the needs of both retail and corporate banking software sectors. At Datavision, our mission is clear: to provide our clients with the best banking software products, ensuring that they stay ahead in an ever-evolving financial landscape. We take pride in serving our prestigious clients and look forward to continuing our journey of innovation and excellence.
Our portfolio of banking software product and services include:
Core Banking Solutions: | FinNext Core | Banking: | FinTrade | EasyLoan | MicroFin |
Digital Banking Solutions: | IBanc | MobiBanc | MBranch | FinTab | FinSight |
Risk & Compliance: |FinTrust |
Want to know how our team of experts at Datavision provides customizable, scalable, and cost-effective banking software products and solutions to our esteemed clients? Visit us for more information.